Haptic Technology Innovations 2025: U.S. Digital Experience

Haptic technology innovations are rapidly transforming U.S. digital experiences, with five key areas poised for significant impact by 2025, offering enhanced immersion and interaction across diverse industries.
The Rise of Haptic Technology: 5 Innovations Transforming U.S. Digital Experiences by 2025 (RECENT UPDATES, COMPARISON/ANALYSIS) is no longer a futuristic concept but a rapidly evolving reality, fundamentally reshaping how Americans interact with digital content and devices. From immersive gaming to critical medical training, haptic feedback is moving beyond simple vibrations to sophisticated tactile sensations, promising a richer, more intuitive digital landscape. This report delves into the current trajectory and anticipated impact of these groundbreaking developments, focusing on what consumers and industries can expect in the very near future.
The Evolution of Haptic Feedback: Beyond Simple Vibrations
Haptic technology, traditionally associated with basic vibrations in mobile phones and game controllers, is undergoing a profound transformation. Modern advancements are enabling far more nuanced and precise tactile sensations, simulating textures, pressures, and even the feeling of impact. This evolution is driven by breakthroughs in materials science, miniaturization, and sophisticated algorithms that translate digital information into physical touch. The goal is to bridge the gap between the digital and physical worlds, making virtual interactions feel as real and intuitive as possible. This paradigm shift holds immense implications for user engagement and the design of digital interfaces across various sectors.
Recent updates indicate a strong focus on developing highly localized and variable haptic responses. Instead of a uniform buzz, devices are now capable of delivering distinct sensations to specific areas of the hand or body, mimicking the intricate details of physical contact. This level of fidelity is critical for applications that demand high precision and immersion. According to industry analysts, the market for advanced haptic solutions is projected to grow significantly, fueled by demand from consumer electronics, automotive, and healthcare sectors. The comparison to older haptic systems highlights a move from mere notification to genuine interaction, creating a more sensory-rich digital experience for users across the United States.
From Basic Buzz to Complex Textures
- Piezoelectric Actuators: These tiny, energy-efficient devices allow for much finer control over haptic sensations, enabling the simulation of distinct textures and subtle pressures, a significant leap from traditional eccentric rotating mass (ERM) motors.
- Electro-tactile Stimulation: By applying small electrical currents to the skin, this method can create the sensation of different textures or even temperature changes without physical movement, opening new avenues for interactive displays and wearables.
- Surface Haptics: Technologies like ultrasonic vibration or electrovibration modify the friction between a finger and a screen, allowing users to ‘feel’ virtual buttons, textures, or even the edges of digital objects directly on a flat surface.
The analysis of these foundational technologies reveals a clear trend towards greater realism and versatility. The ability to render complex tactile feedback is not just about entertainment; it’s about enhancing functionality, safety, and accessibility in digital environments. As these technologies mature, their integration into everyday devices will become seamless, fundamentally altering our perception and interaction with the digital realm.
Immersive Gaming and Entertainment: A New Dimension of Play
The gaming industry has long been a pioneer in adopting haptic feedback, but the innovations arriving by 2025 are set to elevate immersion to unprecedented levels. Beyond traditional rumble, next-generation haptic devices will integrate into peripherals like controllers, VR headsets, and even full-body suits, delivering detailed tactile sensations that mirror in-game events. Imagine feeling the recoil of a weapon, the texture of a virtual surface, or the impact of a collision with startling realism. This enhanced sensory input is crucial for creating truly believable virtual worlds and significantly deepening player engagement.
Recent updates from major gaming hardware manufacturers confirm a concerted effort to standardize and expand haptic capabilities. New controllers are incorporating advanced actuators that can provide nuanced feedback, distinguishing between different types of terrain, weapon impacts, and environmental effects. This level of detail offers a competitive edge in esports and transforms single-player narratives into visceral experiences. The comparison with current systems highlights a move from generic feedback to context-aware sensations, where every in-game action has a corresponding, unique physical response. For U.S. gamers, this means a more profound connection to their digital adventures.
Key Advancements in Gaming Haptics
- Adaptive Triggers: Controllers featuring triggers that dynamically adjust resistance and vibration based on in-game actions, simulating the tension of a bowstring or the crunch of a brake pedal.
- Directional Haptics: The ability to feel impacts or sensations originating from specific directions, enhancing spatial awareness and realism in virtual environments.
- Haptic Vests and Suits: Wearable devices that provide full-body feedback, allowing users to feel impacts, environmental effects (like wind or rain), and even the presence of virtual objects on their torso and limbs.
This analysis underscores how haptic technology is becoming an indispensable component of next-generation gaming. The drive for hyper-realism and deeper immersion is pushing developers and hardware manufacturers to innovate rapidly, ensuring that the digital playground of 2025 will be a truly multi-sensory experience for players across the United States. The blend of visual, auditory, and tactile feedback will create digital worlds that are not just seen and heard, but genuinely felt.

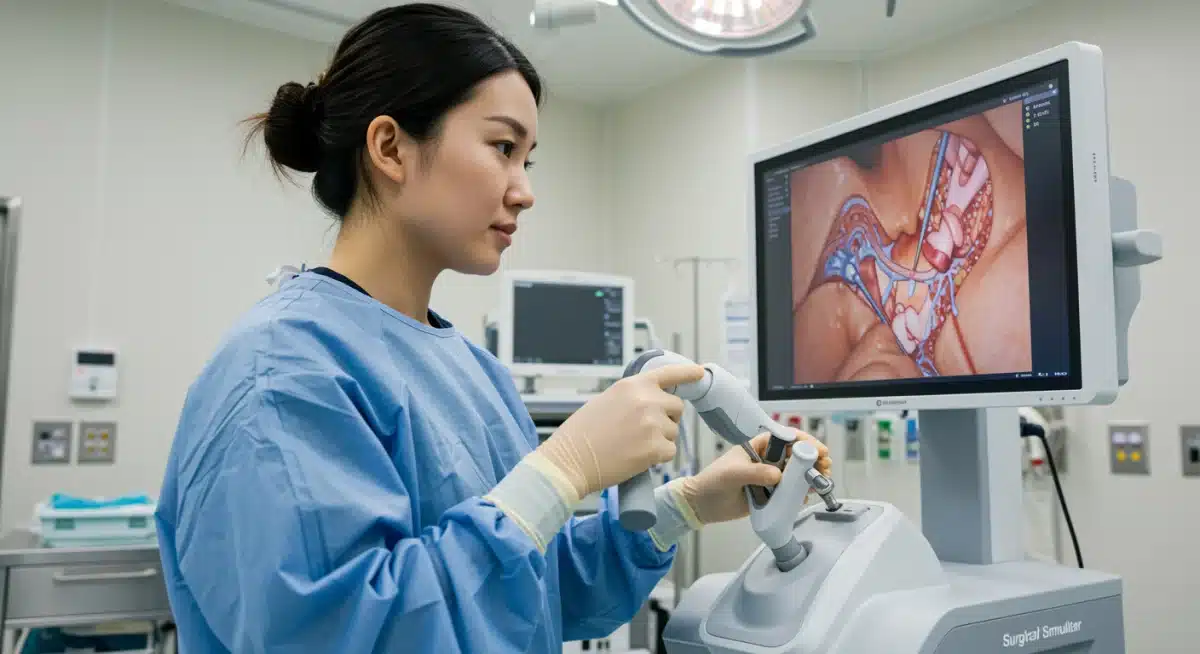
Healthcare and Medical Training: Precision Through Touch
The application of haptic technology in healthcare is poised to revolutionize medical training and surgical procedures by 2025. By providing realistic tactile feedback, haptic systems enable aspiring surgeons to practice complex operations in a risk-free virtual environment, feeling the resistance of tissues, the texture of organs, and the precision required for delicate maneuvers. This significantly enhances skill acquisition and reduces the learning curve for new techniques, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. The ability to simulate various medical scenarios with high fidelity offers an invaluable tool for continuous professional development.
Recent updates from medical simulation companies highlight the integration of advanced haptics into robotic surgery systems and diagnostic tools. Surgeons can now experience force feedback during minimally invasive procedures, allowing them to ‘feel’ internal structures without direct physical contact. This not only improves precision but also reduces surgeon fatigue. A comparison with traditional training methods reveals that haptic-enabled simulators offer a more consistent and measurable learning experience, allowing for objective assessment of proficiency. For U.S. medical institutions, this means a new era of highly effective and safe training protocols, preparing the next generation of healthcare professionals with unparalleled tactile skills.
Haptic Applications in Medicine
- Surgical Simulators: Systems that replicate the tactile sensations of cutting, suturing, and manipulating tissues, providing realistic practice for various surgical disciplines, from laparoscopy to ophthalmology.
- Rehabilitation Devices: Haptic feedback incorporated into physical therapy tools can guide patients through exercises, providing gentle resistance or cues to improve motor control and recovery from injuries.
- Diagnostic Tools: Future diagnostic devices may use haptics to allow physicians to ‘palpate’ virtual models of organs, detecting abnormalities or tumors with greater sensitivity and precision.
The analysis indicates that haptic technology is moving beyond simulation to become an integral part of actual medical intervention and diagnostics. The emphasis on precision and realism means that medical practitioners will have access to tools that extend their sensory capabilities, leading to more accurate diagnoses and safer, more effective treatments. This represents a critical advancement in U.S. healthcare, promising improved standards of care and training.
Automotive Industry: Enhanced Safety and Intuitive Control
The automotive sector is rapidly integrating haptic technology to enhance driver safety, improve human-machine interfaces, and create a more intuitive driving experience by 2025. Haptic feedback in steering wheels, seats, and pedals can provide non-visual alerts for potential hazards, such as lane departure warnings or collision alerts, without distracting the driver’s eyes or ears. This subtle yet effective form of communication is crucial in reducing cognitive load and improving reaction times, especially as vehicles become more autonomous and complex.
Recent developments from leading automotive manufacturers showcase advanced haptic features in their latest models. Steering wheels can vibrate to indicate a drifting lane, while seats can buzz on the left or right to warn of objects in blind spots. An analysis of these systems reveals that haptic warnings are often processed faster than auditory or visual cues, making them highly effective in critical situations. Furthermore, haptics are being used to create more tactile and responsive infotainment systems, allowing drivers to ‘feel’ virtual buttons or navigate menus without looking away from the road. This comparison with traditional warning systems highlights a significant leap in driver assistance. For U.S. drivers, this translates into safer roads and a more comfortable, intuitive interaction with their vehicles.
Haptic Innovations in Vehicles
- Tactile Warnings: Steering wheel or seat vibrations that alert drivers to lane departures, potential collisions, or blind spot intrusions, providing immediate and intuitive feedback.
- Haptic Infotainment Controls: Touchscreens that provide tactile feedback, mimicking the feel of physical buttons or sliders, allowing for safer interaction without visual distraction.
- Pedal Haptics: Accelerator pedals that vibrate or provide resistance to warn drivers of excessive speed, impending collisions, or to guide them towards optimal fuel efficiency.
This overview demonstrates how haptic technology is not merely an add-on but a fundamental component of next-generation vehicle design. The focus on safety, combined with the drive for intuitive controls, positions haptics as a key enabler for smarter, safer, and more user-friendly automobiles in the U.S. market. The integration of these systems will make driving a more informed and less stressful experience for millions.
Consumer Electronics and Wearables: Seamless Everyday Interaction
By 2025, haptic technology will deeply embed itself within everyday consumer electronics and wearables, transforming how Americans interact with their devices and digital information. Beyond simple smartphone vibrations, expect smartwatches that provide nuanced tactile alerts, headphones that deliver haptic feedback for spatial audio, and even smart clothing that offers physical cues for navigation or fitness tracking. These subtle yet powerful integrations aim to make technology more intuitive, less intrusive, and seamlessly integrated into daily life, moving towards a world where digital interactions are felt rather than just seen or heard.
Recent updates in wearable technology indicate a strong push for miniaturized, low-power haptic actuators that can be incorporated into a wide range of devices without sacrificing battery life or form factor. For instance, smart rings could provide discrete notifications through unique vibration patterns, while AR/VR glasses might offer tactile sensations to enhance virtual object interaction. The comparison with current consumer devices reveals a shift from generic alerts to personalized, context-aware tactile communication. This means that a specific vibration might signify an urgent email, while another distinct pattern could alert you to a message from a family member. For U.S. consumers, this promises a more personal and less distracting way to stay connected and informed.
Integrating Haptics into Daily Devices
- Smartwatches and Rings: Delivering discreet, personalized notifications through unique vibration patterns, enhancing privacy and reducing reliance on visual or auditory alerts.
- Haptic Headphones: Providing tactile feedback that complements audio, enhancing bass, spatial awareness, and immersion in music, gaming, and virtual reality content.
- Smart Clothing: Garments embedded with haptic elements that can guide users with directional cues during navigation, provide feedback during fitness routines, or even offer therapeutic massage.
This analysis highlights the pervasive potential of haptic technology to enrich daily interactions. As devices become smaller and more integrated, haptics will play a crucial role in making technology feel more natural and intuitive. The goal is to create a digital experience that is not only functional but also deeply felt and understood, making consumer electronics an extension of our senses rather than mere tools.
Accessibility and Inclusivity: Empowering All Users
One of the most significant and often overlooked impacts of advanced haptic technology by 2025 will be its role in enhancing accessibility and inclusivity for users with disabilities. Haptic feedback can provide critical sensory information that might otherwise be unavailable, opening up new avenues for interaction and engagement with digital content. For individuals with visual impairments, haptic cues can translate on-screen information into discernible tactile patterns, guiding navigation, conveying data, and enriching multimedia experiences. Similarly, for those with hearing impairments, haptics can provide non-auditory alerts and feedback, making digital communication more comprehensive.
Recent updates in assistive technology show a growing focus on integrating sophisticated haptic interfaces into devices designed for diverse needs. Tactile displays, for example, are evolving to render complex graphical information as dynamic textures and shapes that can be felt. This allows visually impaired users to interpret charts, maps, and even images. An analysis of these developments indicates that haptics offers a powerful alternative or complement to existing assistive technologies, providing a richer, more direct form of communication. The comparison with purely audio-based or screen-reader solutions demonstrates how haptics can provide a more immediate and intuitive understanding of digital environments. For U.S. communities focused on inclusivity, haptic technology presents a transformative tool for digital empowerment.
Haptic Solutions for Accessibility
- Tactile Navigation: Haptic feedback in smartphones and wearables can provide directional cues through vibrations, guiding visually impaired users through unfamiliar environments.
- Data Visualization: Tactile screens or devices that translate complex data, charts, and graphs into discernible haptic patterns, making information accessible to a wider audience.
- Communication Aids: Haptic feedback can complement or replace auditory alerts, providing non-visual cues for notifications, messages, and even emotional context in digital interactions.
This overview emphasizes the profound social impact of haptic technology in fostering a more inclusive digital world. By transforming visual and auditory information into tactile experiences, haptics empowers individuals with various disabilities to engage more fully and independently with technology. The ongoing innovations are not just about convenience but about fundamental access and equal opportunity in the digital age, a crucial development for the U.S. in the coming years.
| Key Innovation Area | Impact by 2025 |
|---|---|
| Immersive Gaming | Unprecedented realism, deeper player engagement with nuanced tactile feedback. |
| Healthcare Training | Enhanced surgical precision, realistic medical simulation, improved skill acquisition. |
| Automotive Safety | Intuitive non-visual alerts, improved driver-vehicle interaction, enhanced road safety. |
| Consumer Wearables | Seamless, personalized, and less intrusive digital interactions in daily life. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Haptic Technology
▼
Haptic technology provides tactile feedback, simulating sensations of touch through vibrations or forces. It’s evolving from simple buzzes to nuanced textures and pressures, driven by advanced actuators and algorithms, creating more realistic and immersive digital interactions.
▼
By 2025, haptics will deliver unprecedented realism in gaming, allowing players to feel in-game events like weapon recoil or terrain textures through adaptive controllers and full-body suits, significantly deepening immersion and player engagement.
▼
In healthcare, haptics enable realistic surgical training by simulating tissue resistance and organ textures in virtual environments. This enhances skill acquisition, reduces learning curves for new techniques, and improves overall patient safety and outcomes.
▼
Haptic feedback in vehicles provides non-visual alerts for hazards like lane departures or blind spot objects through subtle vibrations in steering wheels or seats. This helps drivers react faster, reduces distractions, and enhances overall road safety.
▼
Absolutely. Haptic technology offers critical sensory information for users with disabilities, translating visual data into tactile patterns for the visually impaired and providing non-auditory alerts for the hearing impaired, fostering greater inclusivity in digital experiences.
Outlook: The Future is Felt
The acceleration of Haptic Technology advancements makes it clear that the future of digital interaction will be defined not only by what we see or hear, but by what we physically feel. As Haptic Technology evolves across immersive gaming, healthcare simulation, automotive safety systems, consumer gadgets e soluções de acessibilidade, it becomes evident that these innovations are only the foundation of a much deeper transformation. Especialistas já destacam esse movimento em análises dedicadas à expansão da Haptic Technology, como no conteúdo publicado pela MassChallenge, que explora o impacto crescente dessa área — veja mais nessa referência sobre Haptic Technology.
By 2025, Haptic Technology is expected to deliver hyper-personalized and adaptive tactile feedback, reshaping the U.S. digital experience with interfaces that respond dynamically to user intention and emotion. As actuators become more compact and algorithms more intelligent, Haptic Technology will blur the boundary between physical and virtual environments, transforming everyday interactions into deeply sensory, emotionally engaging experiences. The future of connectivity will not just be intelligent — with Haptic Technology, it will be truly felt.