Cybersecurity Guide 2025: Zero Trust Architecture in 90 Days

Implementing a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is crucial for modern cybersecurity, and this guide provides a roadmap for organizations to adopt ZTA principles effectively within a 90-day timeframe, enhancing their security posture against evolving threats in 2025.
Is your organization ready to face the cybersecurity challenges of 2025? The threat landscape is constantly evolving, demanding a more proactive and robust approach to security. This Cybersecurity Guide 2025: Implement Zero Trust Architecture in 90 Days will provide you with a clear, actionable plan to strengthen your defenses and protect your valuable assets.
Understanding the Need for Zero Trust in 2025
The year 2025 is poised to bring even more sophisticated cyber threats. Traditional security models, which operate on the principle of “trust but verify,” are no longer sufficient. A Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) offers a more secure and adaptable framework to protect against these evolving dangers.
Adopting ZTA isn’t just a recommendation; it’s a necessity for organizations aiming to maintain a strong security posture in the face of increasingly complex and frequent cyberattacks.
The Limitations of Traditional Security Models
Traditional security models often rely on perimeter-based defenses, creating a “castle-and-moat” approach. Once an attacker breaches the perimeter, they have relatively free rein within the network. This is where Zero Trust comes into play.
- Implicit Trust: Traditional models grant implicit trust to users and devices inside the network.
- Perimeter Focus: Emphasis is placed on securing the network perimeter, neglecting internal vulnerabilities.
- Lateral Movement: Attackers can easily move laterally within the network once they bypass the perimeter.
Zero Trust fundamentally changes this approach by eliminating implicit trust and continuously verifying every user and device, regardless of their location.
In conclusion, understanding the shortcomings of traditional security models highlights the urgent need for Zero Trust Architecture, especially as we approach the cybersecurity landscape of 2025.
Key Principles of Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture is built on several core principles that challenge traditional security assumptions. Understanding these principles is crucial for successful implementation.
By embracing these tenets, organizations can develop a more resilient and adaptable security framework that can withstand the evolving threats of 2025.
Verify Explicitly
Every user, device, and application must be authenticated and authorized before being granted access to any resource. This principle eliminates the concept of implicit trust, ensuring that only verified entities can access sensitive data and systems.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA for all users, requiring multiple forms of verification.
- Device Authentication: Verify the identity and security posture of every device attempting to access the network.
- Application Authorization: Control which applications are allowed to access specific resources.
Explicit verification is the cornerstone of Zero Trust, providing a strong foundation for a more secure environment.
Least Privilege Access
Grant users and applications only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks. This principle limits the potential damage caused by a compromised account or application.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign access based on job roles, rather than individual needs.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Access: Grant temporary access to resources only when needed.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Control and monitor access to privileged accounts.
Least privilege access significantly reduces the attack surface and limits the impact of security breaches.
In essence, the key principles of Zero Trust Architecture – explicit verification and least privilege access – create a security framework that is both robust and adaptable to the ever-changing threat landscape.
Assessing Your Current Security Posture
Before implementing Zero Trust Architecture, it’s essential to assess your current security posture. This involves identifying existing vulnerabilities, evaluating security controls, and understanding your organization’s risk profile.
A thorough assessment will provide a clear baseline for measuring progress and ensuring that your Zero Trust implementation is tailored to your specific needs.
Start by conducting a comprehensive security audit. This audit should cover all aspects of your IT infrastructure, including:
- Network Infrastructure: Evaluate the security of your network devices, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
- Endpoint Security: Assess the security of your laptops, desktops, and mobile devices.
- Data Security: Identify sensitive data and evaluate the effectiveness of data protection measures.
Identifying Critical Assets
Knowing what to protect is just as important as knowing how to protect it. Identifying your organization’s critical assets is a fundamental step in the Zero Trust journey.
Critical assets typically include:
- Customer Data: Personally identifiable information (PII) and financial data.
- Intellectual Property: Trade secrets, patents, and proprietary information.
- Financial Records: Accounting data, financial statements, and transaction records.
Identifying these assets allows you to prioritize security efforts and allocate resources effectively.
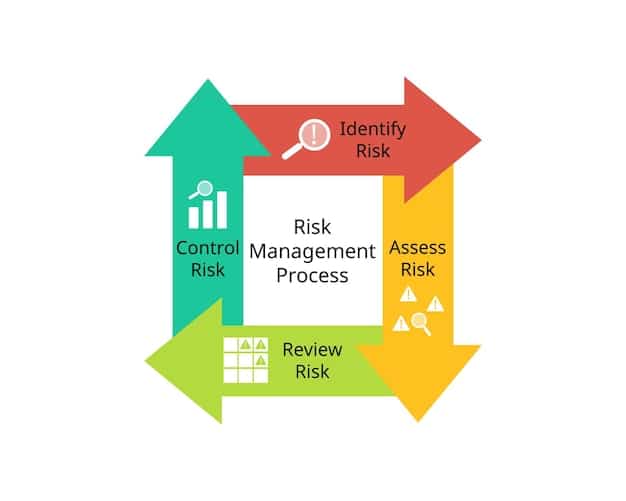
Assessing your security posture is a crucial step in the Zero Trust implementation process. By understanding your current state, you can create a targeted and effective plan to strengthen your security defenses.
Planning Your Zero Trust Implementation
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It requires careful planning and a phased approach to ensure successful integration with your existing infrastructure.
Consider using a phased approach, starting with a small pilot project and gradually expanding the scope of implementation. This allows you to test and refine your approach before rolling it out across the entire organization.
Defining Clear Objectives
Before embarking on your Zero Trust journey, define clear and measurable objectives. What specific security outcomes do you want to achieve?
Example objectives:
- Reduce the risk of data breaches by 50% within one year.
- Improve compliance with industry regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA.
- Enhance visibility into network activity and user behavior.
Clear objectives will help you stay focused and track your progress.
Selecting the Right Technologies
Numerous security technologies can support your Zero Trust implementation. Choosing the right tools is essential for achieving your objectives.
Some key technologies to consider:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Centralizes user identity and access control.
- Microsegmentation: Divides the network into small, isolated segments.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Collects and analyzes security logs from various sources.
Planning your Zero Trust implementation requires careful consideration of your objectives, budget, and existing infrastructure. By taking a phased approach and selecting the right technologies, you can ensure a successful and effective implementation.
Implementing Zero Trust in 90 Days: A Roadmap
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture can seem daunting, but it is achievable within a 90-day timeframe with a structured approach. This roadmap provides a step-by-step guide to help you get started.
This roadmap is designed to provide a clear and actionable plan for implementing Zero Trust Architecture within 90 days. However, remember that every organization is different, and you may need to adjust the timeline and activities based on your specific needs and resources.
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Weeks 1-3)
The first phase focuses on assessing your current security posture, defining your Zero Trust objectives, and selecting the right technologies.
Key activities include:
- Conducting a comprehensive security audit.
- Identifying critical assets and data.
- Defining clear Zero Trust objectives.
- Selecting the appropriate security technologies.
Phase 2: Implementation and Configuration (Weeks 4-9)
The second phase involves implementing and configuring the selected security technologies.
- Deploying IAM solutions and implementing MFA.
- Implementing microsegmentation to isolate critical assets.
- Configuring SIEM tools to collect and analyze security logs.
Phase 3: Monitoring and Optimization (Weeks 10-12)
The final phase focuses on monitoring the effectiveness of your Zero Trust implementation and making necessary adjustments.
- Monitoring network activity and user behavior.
- Analyzing security logs and incident reports.
- Optimizing security policies and configurations.
Implementing Zero Trust in 90 days requires dedication and a structured approach. By following this roadmap, you can make significant progress in strengthening your organization’s security posture.
Tools and Technologies for Zero Trust
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture requires the right tools and technologies to enforce its principles. Several solutions can help organizations achieve Zero Trust security.
Selecting the right tools is crucial for a successful Zero Trust implementation. Consider your organization’s specific needs and budget when evaluating different options.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM solutions are essential for controlling user identities and access privileges. They provide a centralized platform for managing user accounts, authentication, and authorization.
Key features of IAM solutions:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Microsegmentation
Microsegmentation divides the network into small, isolated segments, limiting the lateral movement of attackers. This approach reduces the impact of security breaches by containing them within a specific segment.
Benefits of microsegmentation:
- Reduced Attack Surface
- Improved Incident Response
- Enhanced Visibility
Choosing the appropriate tools and technologies is critical for successfully implementing Zero Trust Architecture. By carefully evaluating your options, you can build a robust and effective security framework.
Measuring the Success of Your Zero Trust Implementation
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture is an ongoing process, and it’s essential to measure its success to ensure that it’s achieving its intended outcomes. This involves tracking key metrics and regularly evaluating your security posture.
Regular monitoring and evaluation will help you identify areas for improvement and ensure that your Zero Trust implementation remains effective over time.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the effectiveness of your Zero Trust implementation.
Example KPIs:
- Reduction in the number of security incidents.
- Improvement in compliance with industry regulations.
- Increased visibility into network activity and user behavior.
Regular Security Audits
Conduct regular security audits to evaluate your security posture and identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Penetration testing
- Vulnerability scanning
- Security awareness training
Measuring the success of your Zero Trust implementation is crucial for ensuring its effectiveness. By tracking KPIs and conducting regular security audits, you can continuously improve your security posture and protect your organization from evolving threats.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🔑 Zero Trust Principles | Verify explicitly, ensure least privilege, assume breach. |
| 🛡️ Assessment & Planning | Identify assets, assess posture, define objectives. |
| 🚀 90-Day Roadmap | Structured implementation phases for quick results. |
| 📊 Measuring Success | Track KPIs, conduct audits, stay adaptable. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
Zero Trust is a security model based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It assumes that no user or device should be trusted by default, whether inside or outside the network perimeter.
▼
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, traditional security models are no longer sufficient. Zero Trust provides a more robust and adaptable framework to protect against evolving dangers.
▼
While full implementation can take time, this guide provides a roadmap for achieving significant progress within 90 days, focusing on key areas and a phased approach.
▼
Key tools include Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions, microsegmentation technologies, and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, among others.
▼
Success can be measured through KPIs such as a reduction in security incidents, improved regulatory compliance, and increased visibility into network activity and user behavior.
Conclusion
By embracing the principles outlined in this guide, your organization can take significant steps toward implementing Zero Trust Architecture and strengthening its security posture against the evolving threats of 2025. Start planning today for a more secure tomorrow.





