Cybersecurity Guide: Incident Response Planning – A 2025 Guide

Cybersecurity Guide: Incident Response Planning: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025 navigates the complexities of incident response, offering a detailed roadmap for organizations to prepare for, detect, and recover from cyberattacks effectively.
In today’s digital landscape, cyber threats are constantly evolving, making cybersecurity guide: incident response planning: a comprehensive guide for 2025 crucial for businesses of all sizes. Are you prepared to handle a cyberattack? Let’s explore how to create an incident response plan that will protect your organization in the coming years.
What is Incident Response Planning?
Incident response planning is the process of creating a documented, organized approach to addressing and managing the aftermath of a security breach or cyberattack. It’s more than just having a set of tools; it’s about having a well-defined strategy to minimize damage and recover quickly.
Why is Incident Response Planning Important?
Incident response planning is vital for several reasons. Without a plan, organizations can suffer significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
- Minimizes Downtime: A well-structured plan ensures quick recovery, reducing operational disruptions.
- Reduces Financial Impact: Swift action can limit the financial damage caused by a breach.
- Protects Reputation: Effective incident response can help maintain customer trust and protect your brand.
- Ensures Compliance: Many regulations require organizations to have incident response plans.
Incident response planning is not merely a best practice; it’s a necessity in today’s threat landscape.
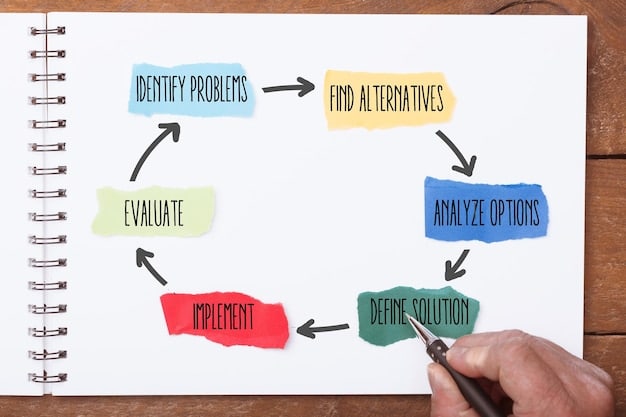
Key Components of an Incident Response Plan
A comprehensive incident response plan includes several essential components. These components ensure that the plan is thorough, actionable, and effective in managing different types of security incidents.
Preparation
Preparation involves establishing the foundation for incident response. This includes developing policies, procedures, and training programs to ensure that the team is ready to respond effectively.
Identification
The identification phase focuses on detecting and analyzing security incidents. This requires implementing monitoring tools, establishing clear reporting channels, and conducting thorough investigations to determine the scope and impact of the incident.
Containment
Containment aims to limit the damage caused by the incident. This phase involves isolating affected systems, preventing further spread of the attack, and taking measures to protect critical assets.
Eradication
Eradication involves removing the cause of the incident and restoring affected systems to a secure state. This phase requires identifying and eliminating the root cause of the attack so that the affected systems return to normal operation.
Recovery
The recovery phase focuses on restoring normal business operations. This involves verifying system functionality, implementing additional security measures, and ensuring that all data is recovered and protected.
Lessons Learned
The lessons learned phase involves documenting the incident, identifying areas for improvement, and updating the incident response plan accordingly. It is crucial to update all relevant teams to increase awareness and readiness.
Each component is integral to the overall success of the incident response plan, ensuring a comprehensive and effective approach to managing security incidents. In today’s ever-evolving cyber threat landscape, this approach is most crucial.
Building Your Incident Response Team
An effective incident response team is crucial for executing your incident response plan. This team should consist of individuals with diverse skills and responsibilities to ensure a well-rounded approach to incident management.
Defining Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly defining roles and responsibilities is the first step in building your incident response team. Common roles include:
- Incident Commander: Leads the team and makes critical decisions.
- Security Analyst: Identifies and analyzes security incidents.
- IT Support: Restores affected systems and ensures network stability.
- Communications Manager: Handles internal and external communications.
Each team member should understand their role and be prepared to execute their responsibilities effectively. Communication lines should remain open, with updates and summaries being passed on.

Tools and Technologies for Incident Response
Leveraging the right tools and technologies is essential for effective incident response. These tools can help you detect, analyze, and respond to security incidents more efficiently.
SIEM Systems
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, providing real-time insights into potential threats. This automation can allow teams to respond proactively.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
EDR tools monitor endpoints for malicious activity, providing detailed information about detected threats and enabling rapid response actions. As endpoints become increasingly targeted, EDR becomes crucial for data security.
Network Traffic Analysis (NTA)
NTA tools analyze network traffic to identify suspicious patterns and anomalies, helping to detect and prevent network-based attacks with automated tracking.
Incident Response Platforms
These platforms coordinate and automate incident response activities, providing a centralized view of ongoing incidents and facilitating collaboration among team members. Incident response platforms can also ensure regulatory compliance.
Effectively utilizing these tools enhances your ability to detect and respond to security incidents, minimizing their impact on your organization.
Incident Response Plan Testing and Training
Regular testing and training are vital to ensure your incident response plan is effective. These activities help identify weaknesses in the plan and prepare the team to respond to real-world incidents.
Tabletop Exercises
Tabletop exercises are simulations that involve discussing hypothetical scenarios to evaluate the plan’s effectiveness. These exercises can help identify gaps in the plan and improve the team’s understanding of their roles.
Simulated Attacks
Simulated attacks involve staging controlled cyberattacks to test the plan’s real-world effectiveness. These attacks can help identify vulnerabilities in your systems and processes.
- Phishing Simulations: Test employees’ ability to recognize and report phishing emails.
- Ransomware Simulations: Evaluate the plan’s ability to contain and recover from a ransomware attack.
- DDoS Simulations: Test the plan’s effectiveness in mitigating a distributed denial-of-service attack.
Regular testing and training ensure that your incident response plan remains effective and that your team is prepared to handle real-world incidents.
Incident Response Planning: A Look into 2025
As we approach 2025, incident response planning must adapt to emerging threats and evolving technologies. Staying ahead of the curve requires understanding the latest trends and incorporating them into your incident response strategy.
Emerging Threats
Several emerging threats will shape incident response planning in 2025, including:
- AI-Powered Attacks: AI can be used to automate and enhance cyberattacks, making them more sophisticated and difficult to detect.
- IoT Vulnerabilities: The increasing number of IoT devices creates new attack vectors for cybercriminals.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Attacks targeting the supply chain can have a wide-ranging impact, affecting numerous organizations simultaneously.
To address these threats, organizations must invest in advanced threat detection capabilities and adopt a proactive approach to security. This can include the use of AI, behavior tracking, and threat intelligence.
Best Practices for Incident Response in 2025
To ensure effective incident response in 2025, consider these best practices:
- Implement Zero Trust Architecture: Verify every user and device before granting access to your network.
- Automate Incident Response: Automate routine tasks to reduce response times and improve efficiency.
- Enhance Threat Intelligence: Leverage threat intelligence to stay informed about the latest threats and vulnerabilities.
By adopting these best practices, organizations can develop a robust and effective incident response plan that protects them from evolving cyber threats in 2025 and beyond.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🛡️ Preparation | Establish policies and training for incident response. |
| 🚨 Identification | Detect and analyze security incidents promptly. |
| 🔒 Containment | Limit the damage by isolating affected systems. |
| 🚀 Recovery | Restore normal operations and verify system functionality. |
FAQ
▼
The first step is preparation, which involves creating policies and setting up training programs to ensure the team is ready for any incident.
▼
Roles to include are an incident commander, security analysts, IT support, and a communications manager to handle internal and external correspondence.
▼
Regular testing ensures the plan is effective and helps identify any weaknesses, making the team better prepared and more responsive in real events.
▼
Automation improves incident response by reducing the time taken to respond to incidents, enhancing the teams efficiency, and freeing personnel for crucial tasks.
▼
A robust incident response plan includes preparation, identification, containment, eradication, recovery, and feedback, each stage ensuring an effective approach.
Conclusion
Effective cybersecurity guide: incident response planning: a comprehensive guide for 2025 is essential for safeguarding your organization against evolving cyber threats. By understanding the key components, building a skilled team, and leveraging the right tools, you can create a robust plan that minimizes the impact of security incidents and ensures business continuity. Stay proactive, stay informed, and stay protected.





