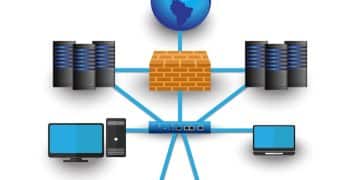
Network Segmentation: A Comprehensive Cybersecurity Guide

Network segmentation is a cybersecurity technique that divides a network into smaller, isolated segments to improve security, control traffic flow, and reduce the scope of potential cyberattacks.
In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity is more critical than ever. A robust defense strategy goes beyond basic firewalls and antivirus software. Network segmentation is a powerful technique that divides your network into smaller, isolated segments. This approach significantly enhances security, limits the impact of breaches, and streamlines network management.
Understanding Network Segmentation
Network segmentation is the practice of dividing a computer network into smaller, more manageable subnetworks or segments. Think of it as creating internal firewalls within your network. This isolation provides numerous security and operational benefits.
By segmenting your network, you can control the flow of traffic between different areas, limiting the potential damage caused by a security breach.
Why Segment Your Network?
There are several compelling reasons to implement network segmentation. Let’s explore some key advantages:
Improved Security: Segmentation reduces the attack surface by limiting the lateral movement of attackers within your network.
Reduced Breach Impact: If one segment is compromised, the attacker’s access is limited to that segment, preventing them from spreading to other critical areas.
Compliance: Segmentation can help meet regulatory compliance requirements, such as PCI DSS and HIPAA, by isolating sensitive data.
- Isolate sensitive data to comply with industry regulations.
- Limit the spread of malware and ransomware.
- Improve incident response by containing breaches quickly.
Network segmentation is a proactive approach to cybersecurity that minimizes risks and enhances overall network resilience.
Benefits of Network Segmentation
Implementing network segmentation brings a wealth of benefits that extend beyond basic security improvements. It’s a strategic approach that can positively impact your organization’s efficiency and compliance posture.
From containing breaches to streamlining compliance audits, the advantages of network segmentation are substantial.
Enhanced Security Posture
By creating isolated segments, you effectively reduce the attack surface. Threat actors can’t easily move laterally, making it more difficult for them to access critical assets.
Better Visibility and Control: Network segmentation provides granular visibility into network traffic, allowing you to monitor and control communication between segments effectively.
Simplified Compliance: Segmentation simplifies the process of meeting regulatory requirements by isolating sensitive data and limiting the scope of compliance audits.
- Improved security posture by reducing the attack surface.
- Simplified compliance processes for regulatory requirements.
- Enhanced network visibility and control for administrators.
Network segmentation is a vital component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, providing tangible improvements to your organization’s security and operational efficiency.
Types of Network Segmentation
Network segmentation can be implemented using various techniques, each offering different levels of isolation and control. Understanding the different types of segmentation is crucial for designing a strategy that meets your specific needs.
From physical separation to virtualized solutions, the options are diverse and can be tailored to your environment.
Physical Segmentation
Physical segmentation involves using separate physical hardware to create isolated networks. This approach provides the strongest level of isolation but can be more complex and costly to implement.
VLAN Segmentation: Virtual LANs (VLANs) allow you to create logical networks within a single physical network. VLANs are a popular and cost-effective way to segment a network.
Microsegmentation: This advanced technique creates highly granular segments, often down to the individual workload level. It’s especially useful in virtualized and cloud environments.
- Physical segmentation using separate hardware for maximum isolation.
- VLAN segmentation for cost-effective logical network separation.
- Microsegmentation for granular control in virtualized environments.
Selecting the right type of network segmentation depends on your organization’s needs, resources, and security requirements. Each method offers a unique set of advantages and considerations.
Implementing Network Segmentation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing network segmentation requires careful planning and execution. A phased approach ensures minimal disruption to your operations while maximizing the benefits of segmentation.
This step-by-step guide provides a framework for implementing network segmentation effectively.
Step 1: Assess Your Network
Start by conducting a thorough assessment of your network to identify critical assets, sensitive data, and potential vulnerabilities.
Step 2: Define Segmentation Goals: Clearly define your segmentation goals. What are you trying to protect? What compliance requirements do you need to meet?
Step 3: Design Your Segmentation Strategy: Based on the assessment and goals, design a segmentation strategy that outlines how you will divide your network into segments.

- Assess your network to understand critical assets and vulnerabilities.
- Define clear goals for segmentation, such as compliance or data protection.
- Design a strategy that aligns with your goals and network infrastructure.
Effective implementation of network segmentation requires a structured approach, starting with a thorough assessment and ending with ongoing monitoring and maintenance.
Best Practices for Network Segmentation
To maximize the effectiveness of network segmentation, it’s essential to follow industry best practices. These guidelines ensure that your segmentation strategy is robust, manageable, and sustainable.
From least privilege access to regular monitoring, these practices will help you maintain a secure and efficient network.
Least Privilege Access
Implement the principle of least privilege, granting users and devices only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks.
Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor network traffic between segments to detect anomalies and potential security threats.
- Apply the principle of least privilege to limit access within segments.
- Monitor network traffic regularly for anomalies and threats.
- Keep your segmentation strategy up-to-date with changing business needs.
Adhering to best practices ensures that your network segmentation strategy remains effective and adaptable in the face of evolving threats.
Challenges and Considerations
While network segmentation offers significant benefits, it also presents certain challenges and considerations. Addressing these issues proactively is crucial for successful implementation.
From complexity to performance impact, it’s important to be aware of the potential hurdles and plan accordingly.
Complexity
Implementing and managing network segmentation can be complex, especially in large and dynamic environments. Ensure you have the necessary expertise and tools.
Management Overhead: Maintaining a segmented network requires ongoing monitoring and management. Automate tasks where possible to reduce administrative burden.
Performance Impact: Segmentation can introduce some performance overhead due to the increased routing and filtering. Optimize your network configuration to minimize this impact.
- Address complexity by planning thoroughly and using the right tools.
- Minimize management overhead through automation and efficient processes.
- Optimize network configuration to mitigate potential performance impacts.
By anticipating and addressing these challenges, you can ensure a smooth and effective network segmentation implementation.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🛡️ Improved Security | Limits attack spread by isolating network segments. |
| 🔒 Compliance | Facilitates meeting regulations by isolating sensitive data. |
| 📈 Better Control | Provides granular visibility and management of network traffic. |
| 🌐 Types | Includes physical, VLAN, and microsegmentation options. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
▼
The primary goal is to enhance security by isolating network segments, limiting the spread of potential breaches and reducing the attack surface.
▼
VLAN segmentation creates logical networks within a single physical network, while physical segmentation uses separate physical hardware for isolation.
▼
Microsegmentation creates highly granular segments, often down to the individual workload level, making it most useful in virtualized and cloud environments.
▼
Monitoring is crucial to detect anomalies and potential security threats by continuously analyzing network traffic between segments, ensuring the effectiveness of segmentation.
▼
Segmentation simplifies compliance by isolating sensitive data, reducing the scope of audits, and meeting requirements like PCI DSS and HIPAA more efficiently.
Conclusion
Network segmentation is a powerful cybersecurity strategy that can significantly enhance your organization’s security posture. By understanding the benefits, types, and best practices of network segmentation, you can effectively protect your critical assets and ensure a more secure and resilient network.